What is a Psychiatrist?
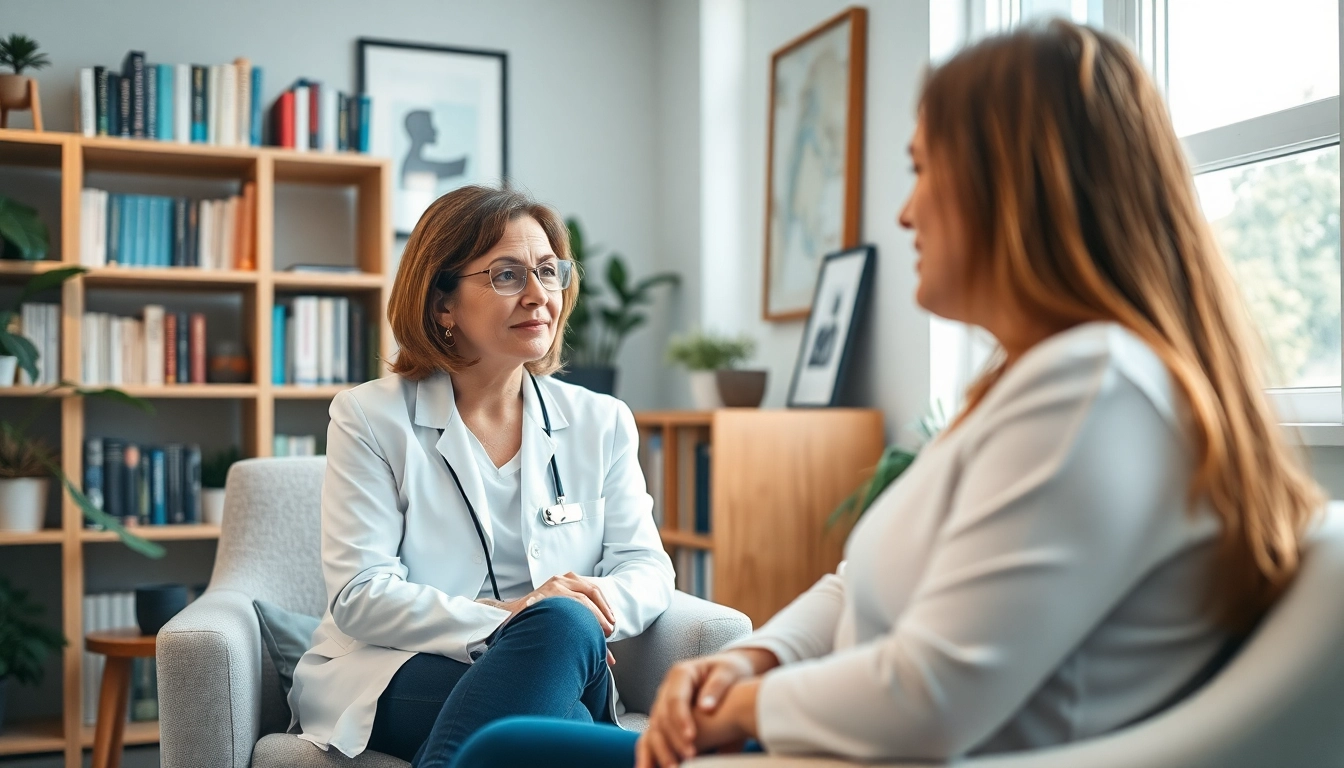
A psychiatrist is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental health conditions. Unlike psychologists, who typically provide therapy and counseling, psychiatrists are qualified to prescribe medication and may also engage in various therapeutic interventions to aid their patients. Their role is crucial in the mental healthcare continuum, addressing a wide array of emotional and behavioral disorders.
To understand the intricate role of a psychiatrist, it’s essential to delve into their qualifications and the scope of their practice.
Definition and Qualifications
To become a psychiatrist, one must complete medical school, followed by a residency in psychiatry which typically lasts four years. During this time, they gain clinical experience in various subfields including adult psychiatry, child and adolescent psychiatry, geriatric psychiatry, neuropsychiatry, and substance abuse. Psychiatrists often hold an M.D. (Doctor of Medicine) or D.O. (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine) degree, equipping them with the knowledge to understand complex interrelations between physical and mental health.
Psychiatrists are trained to assess both the psychological and physiological aspects of mental health conditions, allowing them to provide comprehensive care that includes medication management strategy and therapeutic approaches.
The Specialization of Psychiatry
Psychiatry encompasses a variety of subspecialties which include:
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry: Focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of emotional and behavioral disturbances in younger populations.
- Geriatric Psychiatry: Addresses mental health issues affecting elderly patients, emphasizing cognitive impairment and age-related disorders.
- Forensic Psychiatry: Merges psychiatry and law, assessing individuals involved in legal cases.
- Addiction Psychiatry: Specializes in treating patients suffering from substance abuse and addictive disorders.
- Neuropsychiatry: Focuses on understanding the interrelationship between neurological and psychiatric conditions.
This broad scope allows psychiatrists to tailor their treatment approaches based on specific patient needs, making them integral in managing complex cases that may involve both mental and physical health factors.
Difference Between Psychiatrist and Psychologist
While there is considerable overlap in the domains of psychiatrists and psychologists, the two professions have distinct functions:
- Education: Psychiatrists are medical doctors; psychologists typically hold a Ph.D. or Psy.D. in psychology.
- Medication: Psychiatrists can prescribe medication, while psychologists usually cannot (except in some jurisdictions with additional training).
- Treatment Focus: Psychiatrists often treat mental health disorders with medications and clinical interventions; psychologists primarily provide psychotherapy and behavioral interventions.
Ultimately, both professionals play significant roles in mental health treatment and may work in collaboration to provide comprehensive care.
When to Consult a Psychiatrist
Recognizing when to seek help from a psychiatrist can be pivotal in addressing mental health issues. It is essential to seek assistance if you experience persistent emotional distress or behaviors that interfere with daily living.
Common Signs of Mental Health Issues
Here are some common signs that may indicate the need for psychiatric evaluation:
- Persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness.
- Extreme mood swings or emotional instability.
- Withdrawal from social activities or relationships.
- Difficulties concentrating or making decisions.
- Changes in appetite or sleep patterns.
- Substance abuse as a means to cope.
- Thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
Recognizing these signs early can lead to more effective treatment and improved outcomes.
How a Psychiatrist Can Help
A psychiatrist can offer help through:
- Diagnosis: Performing comprehensive assessments and evaluations to identify mental health conditions.
- Treatment Plan Development: Creating personalized treatment plans that may include therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
- Medication Management: Prescribing appropriate medications and monitoring their effectiveness and side effects.
- Support: Providing therapeutic support through various modalities, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and psychodynamic therapy.
The collaborative nature of psychiatrist-patient relationships ensures that patients feel supported throughout their mental health journeys.
Initial Consultation Expectations
Your first appointment with a psychiatrist will typically include the following:
- Assessment: Detailed discussions about your mental health history, current symptoms, and relevant personal and family medical history.
- Evaluation: Psychological tests or questionnaires may be utilized to gain further insight into your mental health status.
- Treatment Options: Discussion of potential treatment methodologies and the creation of an individualized treatment plan.
- Follow-Up Care: Establishing a plan for ongoing support and revisions to your treatment as necessary.
This initial visit establishes a foundation for the therapeutic relationship and sets the stage for effective care moving forward.
Psychiatric Treatment Approaches
Psychiatrists employ varied approaches to treatment, which may include a blend of medication, therapy, and holistic interventions tailored to individual needs.
Medication Management
Medication is a crucial component for many individuals with mental health conditions. A psychiatrist will assess the appropriate use of medications, which can include:
- Antidepressants: Used to treat depression and anxiety disorders.
- Antipsychotics: Effective in managing symptoms of psychosis and severe mental disorders.
- Stimulants: Commonly prescribed for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- Anxiolytics: Help reduce anxiety in the short term but may not be recommended for long-term use due to dependency risks.
Medication management requires careful monitoring and communication between the psychiatrist and the patient to adjust dosages and assess effectiveness.
Therapeutic Interventions
In conjunction with medication, numerous therapeutic interventions can be employed:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Focuses on understanding and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: Explores underlying emotional conflicts and past experiences that shape current behaviors.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): Emphasizes understanding personal relationships and how they impact treating mental illness.
- Supportive Therapy: Provides emotional support and guidance to help patients cope with challenges.
Choosing the right form of therapeutic intervention is essential to ensure effective outcomes tailored to individual needs.
Holistic Approaches in Psychiatry
Increasingly, psychiatrists are incorporating holistic approaches in their practices. These may include:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Techniques aimed at improving emotional regulation and reducing stress.
- Nutrition and Exercise: Emphasizing the importance of lifestyle choices in maintaining mental health.
- Complementary Therapies: Such as yoga and acupuncture, which may contribute to emotional balance and mental wellness.
Holistic care takes into consideration the whole person, promoting overall health alongside treating specific mental health issues.
Choosing the Right Psychiatrist
Finding the right psychiatrist is a vital step in the mental health journey. Considerations include the psychiatrist’s specialty, approach to treatment, and personal compatibility.
Factors to Consider
When selecting a psychiatrist, consider these factors:
- Specialization: Depending on your specific mental health needs, look for a psychiatrist who specializes in that area.
- Treatment Philosophy: Understand the psychiatrist’s approach to treatment to ensure it aligns with your expectations.
- Location and Availability: Consider the convenience of the psychiatrist’s office location and their availability for appointments.
- Insurance and Fees: Make sure the psychiatrist accepts your insurance or that you are comfortable with out-of-pocket expenses.
Conduct thorough research and, if needed, consult reviews or seek referrals to make informed choices.
Questions to Ask
During your initial consultation, consider asking the psychiatrist the following questions:
- What is your experience in treating my specific mental health condition?
- What treatment options do you recommend, and why?
- How will we evaluate the effectiveness of my treatment?
- Are there any potential side effects of the medications you may prescribe?
These questions will help ensure that you have a clear understanding of your treatment plan and what to expect moving forward.
Checking Credentials and Experience
Verify the psychiatrist’s credentials:
- Ensure they are board-certified in psychiatry by appropriate medical boards.
- Research their training and years of experience in the field.
- Look for any additional certifications or fellowship training in specific areas of psychiatry.
Understanding a psychiatrist’s background can provide confidence in their ability to offer quality care.
The Future of Psychiatry
The field of psychiatry is continuously evolving, marked by innovations and changing societal needs. Understanding these trends can provide insight into the future landscape of mental health care.
Innovative Treatment Trends
Emerging treatment modalities that show promise in psychiatry include:
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): A non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain, shown to be effective for treatment-resistant depression.
- Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy: Research into substances like psilocybin and MDMA for treating PTSD and severe anxiety disorders is gaining traction.
- Mindfulness-Based Interventions: Increasingly integrated into psychiatric practice, mindfulness techniques tout benefits in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Such trends illustrate an ongoing commitment to enhancing treatment efficacy in psychiatry.
Telepsychiatry and Accessibility
The rise of telehealth services has extended psychiatric care to a broader audience:
- Remote consultations can increase accessibility for those in underserved areas or with mobility issues.
- Patients are often more comfortable discussing sensitive issues from the privacy of their home.
- Telepsychiatry can reduce wait times and allow for more flexible appointment scheduling.
This evolution reflects the importance of accessibility in mental health care, promoting the notion that receiving help should be as convenient as possible.
The Role of Technology in Mental Health
Technology is rapidly transforming the mental health landscape:
- Mobile Health Apps: Provide resources for mood tracking, symptom management, and self-care strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence: Developing tools that can assist in diagnosis based on symptom checkers and data analytics.
- Online Support Groups: Facilitate peer support and community while reducing feelings of isolation for individuals with mental health challenges.
The integration of these technologies into psychiatric practices marks a significant shift towards enhancing patient engagement and support.